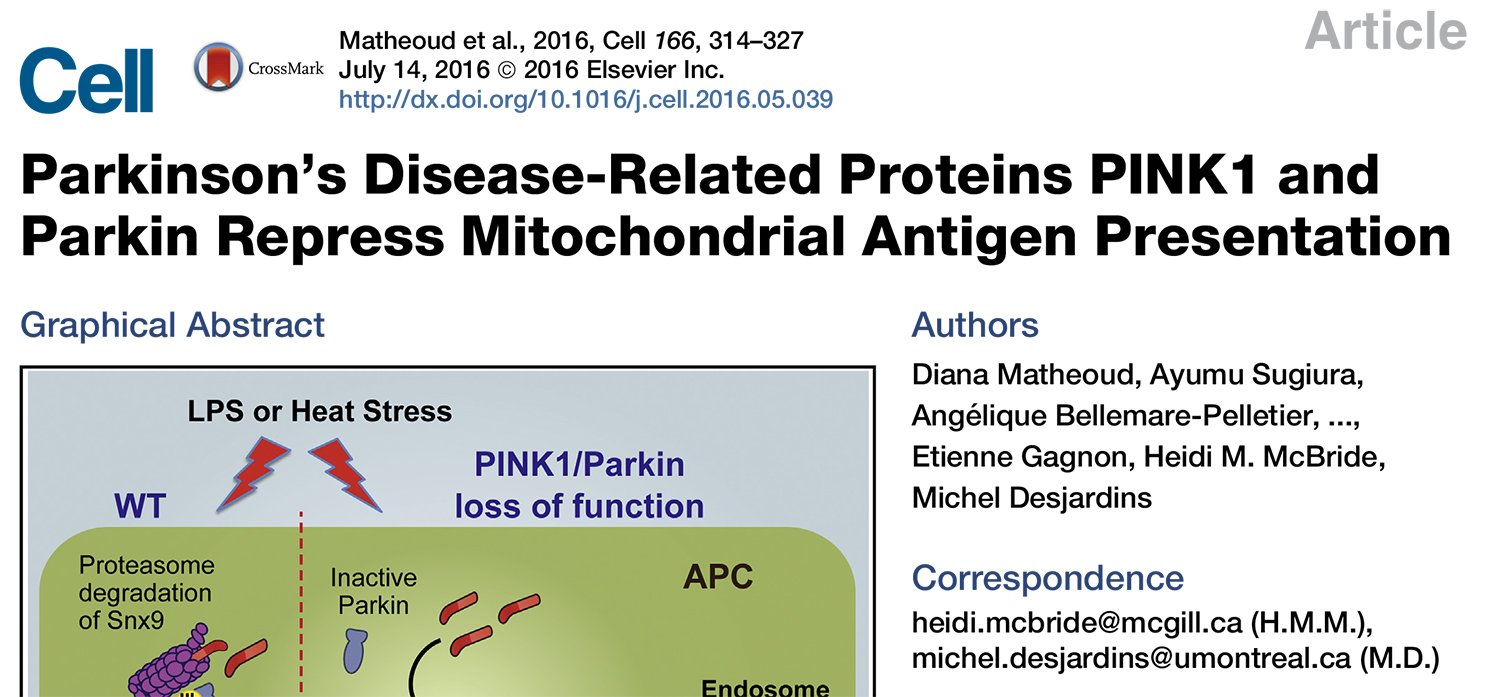
Mitochondria as a platform for immune signaling
Mitochondria play major roles in immune signaling, both viral and during bacterial infections. We have uncovered roles for mitochondrial SUMOylation during antiviral signaling, and demonstrated that mitochondrial derived vesicles are generated following bacterial infection. Vesicles induced upon infection are repressed by PINK1 and Parkin, two Parkinsons related proteins most commonly linked to mitophagy. Our ongoing work attempts to delve deeper into the many roles the mitochondria plays during infection, as we explore new and expanding links to neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinsons Disease.
Most importantly our work in Parkinsons Disease has been done in close collaboration with many labs over the years. Recently we expanded our collaborative team to include 9 different labs across Montreal as we seek to understand the complex events that couple infection to the development of motor symptoms in PD susceptible mouse models. We have a team grant from Aligning Science Across Parkinsons (ASAP) which is allowing us to do some exciting work that we hope to share very soon!